Exercise 6.5
- What is the difference between a class and an object?
- What is the difference between the declaration of a local variable and the
declaration of an instance field?
- What is the difference between a call to a method (as in chapter 5) and a
call to an instance method?
- Suppose that a complex number z = a + bi is represented by an object
of the form shown in the diagram
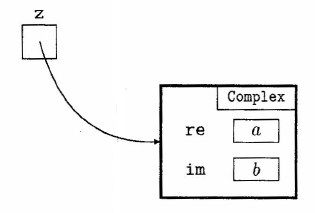
Write a definition for a class Complex that contains
- float fields re and im for the real and imaginary
parts of a number,
- a constructor method that could be called by the statement
Complex z = new Complex(2.7,-1.1);
to create an object that represents the complex number 2.7 - l.li,
- a constructor method with no parameters that creates a Complex
object representing the number 0,
- an instance method that finds the modulus of a complex number,
- an accessor method that returns the value of the real part of a
complex number.
- Suppose that the following fragment is part of a method in the
Complex class developed in the previous question. Draw diagrams
to illustrate the result of executing the fragment.
Complex z1, z2, z3;
z1 = new Complex(2,-2);
z2 = new Complex();
z3 = z1;
z2.re = z3.im + 3;
z2.im = 2*zl.im;
z3.im = z1.re / 2;
- Write a setup method that uses the Fraction class discussed
throughout this chapter. Create a Fraction called f1 that is equal to 2/5.
Create a fraction called f2 that is equal to 3/7. Store the result of
f1squared plus f2 in a Fraction called f3. Print
f3.
- Write a class Lock that could be used to create electronic lock objects.
Each lock may be in either an open (unlocked) or a closed (locked)
state and each one is protected by its own integer key which must be
used to unlock it. The class should contain the following methods.
Lock (int key)
Create a lock that is initially open.void close ()
Close the lock.boolean isOpen ()
Return true if and only if the lock is open.void open (int key)
Open the lock if and only if the parameter key matches the lock's
own key. If the lock is closed and the keys do not match, count
the failed attempt. If the same lock receives three or more failed
attempts in a row, print the message "ALARM".
The following setup method illustrates how the Lock class should work.
void setup ()
{
Lock lock1 = new Lock(111);
Lock lock2 = new Lock(222);
lock1.close();
lock2.close();
println(lock1.isOpen()); // prints false
lock1.open(123); // fails to open lock1
lock1.open(456); // fails to open lock1
lock2.open(222); // opens lock2
lock1.open(789); // fails - prints ALARM
lock1.open(111); // opens lock1
}
- Suppose that rectangles in a Cartesian plane are represented by a
class Rectangle that has four fields as shown:
class Rectangle
{
int left; // x-coordinate of left edge
int bottom; // y-coordinate of bottom edge
int width; // width of rectangle
int height // height of rectangle
- Write a constructor method that has four parameters representing
the four fields of the class. The constructor should replace
any negative length parameters with zero.
- Write a toString method for the Rectangle class. For the rectangle
with lower left corner located at (3,2) and having width 4
and height 5, the method should return "base:(3,2) w:4 h:5".
- Write an instance method, area, that returns the area of a rectangle.
- Write an instance method, perimeter, that returns the perimeter
of a rectangle.
- Write an instance method, contains, that has two explicit parameters
of type int which represent an x and y coordinate. The method should return true
if the point is on the boundary or inside the rectangle determined by the implicit parameter
is on or within the rectangle determined by the implicit
parameter. It should return false otherwise.
|
|